10 March 2025
Retail Lighting Revolutionised

The Impact of Additive Manufacturing on Retail Lighting
10 March 2025
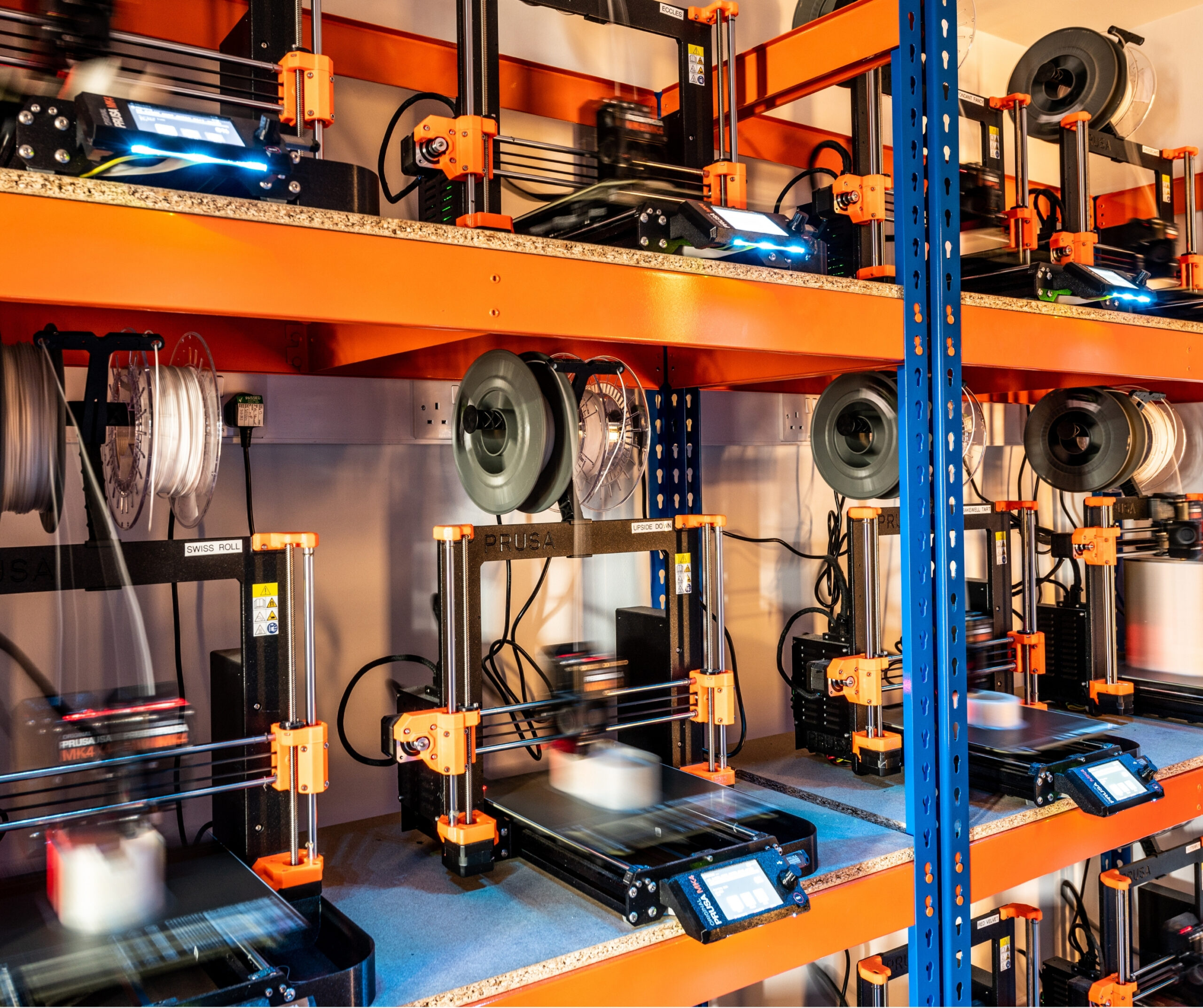
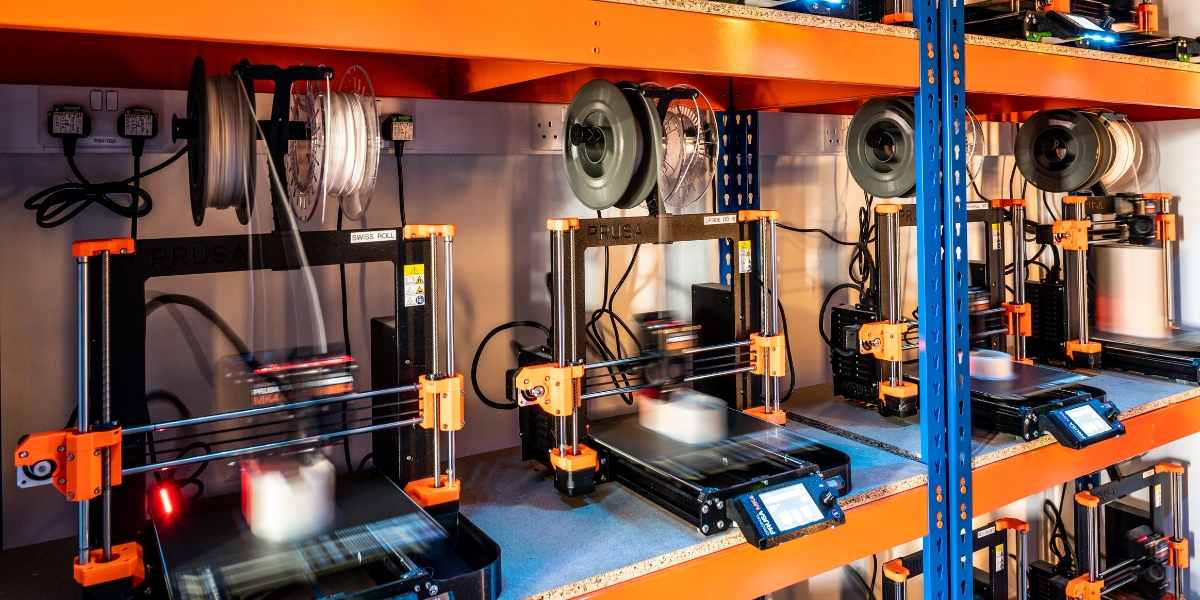
The evolution of manufacturing technologies is transforming industries across the board, and retail lighting is no exception. One of the most significant advancements in recent years is the shift from traditional manufacturing methods to additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing.
This innovation goes beyond adopting modern technology; it redefines how we design, produce, and implement lighting solutions in retail spaces, offering a far more sustainable and efficient approach.
Traditional lighting manufacturing follows a Take, Make, and Waste Model, a linear approach where resources are extracted (taken), transformed into products (made), and eventually discarded (waste). This one-way flow of materials depletes resources and causes environmental degradation.
For decades, retail lighting has been produced using conventional manufacturing techniques. While these methods have been effective in mass production, they have notable drawbacks.
In contrast, additive manufacturing aligns with a circular economy, a more sustainable, cost-effective, and innovative alternative to traditional production methods. Its circular approach minimises waste and makes the most of its resources by designing products for longevity, with repair, reuse, and recycling being central.
Traditional manufacturing involves moulding, casting, and machining. These processes require specialised and costly tooling such as moulds, dies, and cutting instruments, which are essential for shaping and forming materials into precise components. Once a mould or tool is created, design changes become costly and time-consuming, which limits flexibility, innovation and change, often resulting in a business-as-usual approach.
Additive manufacturing uses digital files to eliminate tooling requirements, shorten production times, and reduce costs—especially for small runs and bespoke designs. As technology improves, 3D printing allows manufacturers like us to adapt to new advancements without inhibitive costs so the benefits of these advancements can reach customers more quickly.
Traditional manufacturing’s high production setup and change costs often lead to the use of cheaper, less durable materials or simpler designs. Furthermore, since it is difficult to adjust courses in traditional manufacturing, rapid advancements in technology can quickly render products obsolete.
With its links to the circular economy, additive manufacturing can extend product lifespan and keep products in use longer. Its inherent flexibility supports modular design approaches, allowing easy servicing, repair, or upgrades for products like our lighting fixtures instead of replacement.
Traditional manufacturing processes like casting, moulding, and machining consume large amounts of raw materials and energy. They also produce significant carbon emissions. These methods often involve multiple steps, each with the potential for material loss from steps like cutting or machining. Traditional manufacturing relies heavily on fossil fuels for energy, leading to significant greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change.
The environmental impact of additive manufacturing is significantly lower due to the use of innovative recyclable materials, localised manufacturing, and energy-efficient production methods. This makes 3D printing a key player in cleaning up retail lighting, which traditionally comes at a heavy environmental cost.
Traditional manufacturing leads to overproduction, material waste, and inefficient processes. It also produces toxic by-products that contaminate soil and water sources. Products made with traditional methods are often difficult to reuse or recycle, which means traditional aluminium lighting usually ends up in a landfill.
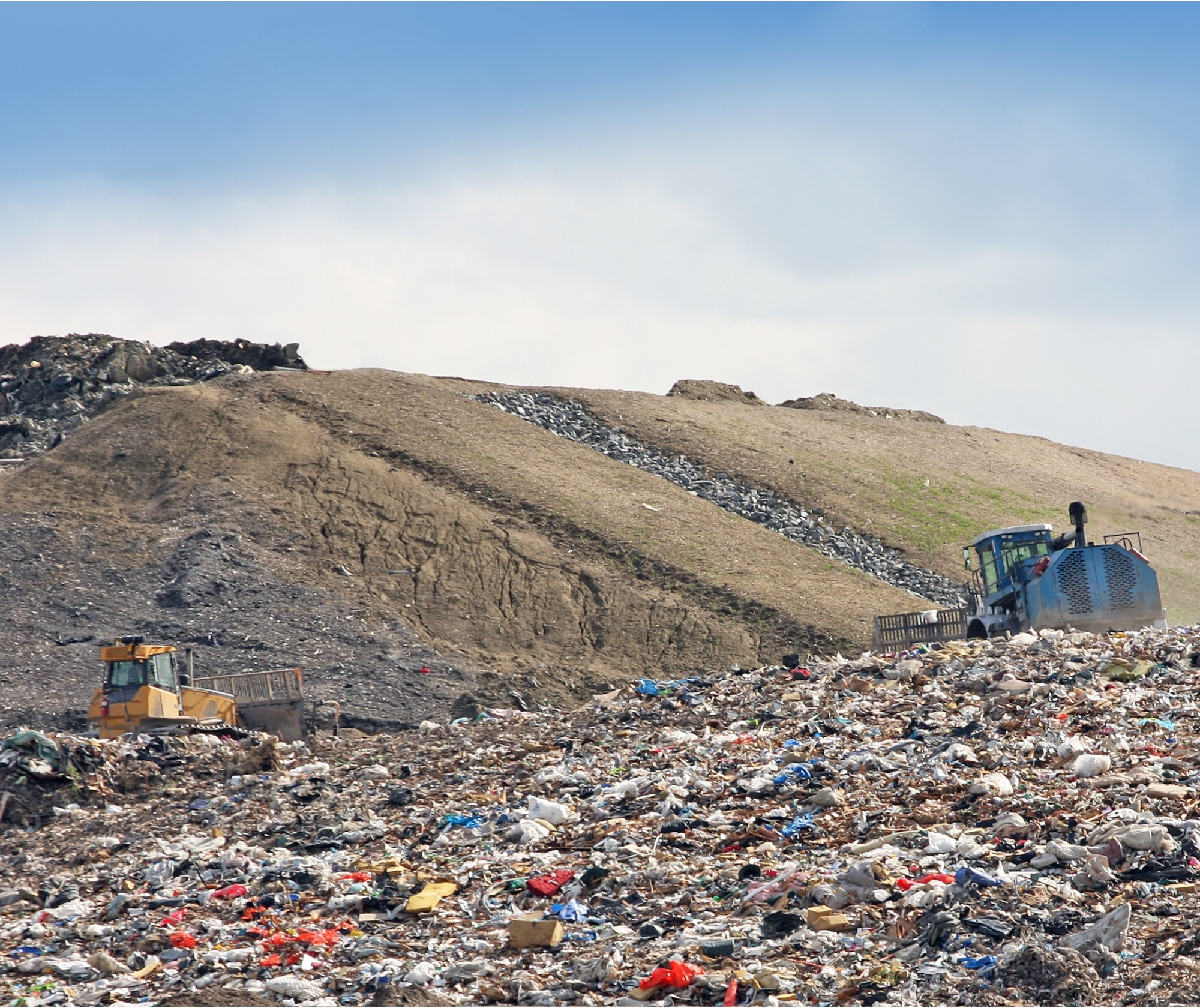

Unlike traditional methods, on-demand 3D printing minimises waste by building objects layer by layer. This approach offers precision and reduces waste. Manufacturers can streamline production processes more easily and use innovative, environmentally friendly materials to eliminate toxic by-products. With circularity built into our additive manufacturing process, we’ll buy back our retail lighting products for reuse and recycling.
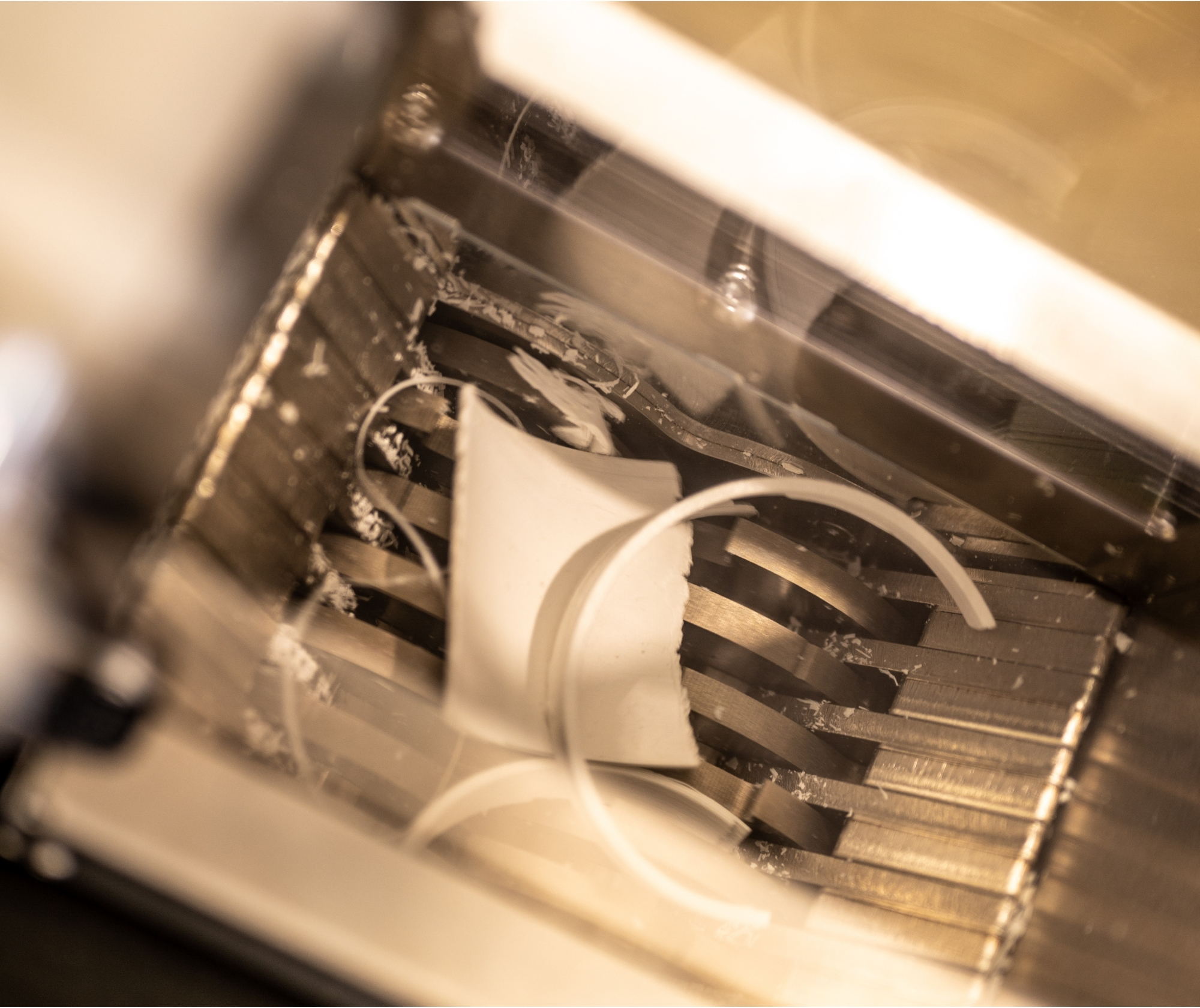
We believe the transition to additive manufacturing is a necessary step towards a more sustainable and innovative future for retail lighting. Our approach reduces carbon emissions while delivering design excellence and efficiency. By embracing innovations in additive manufacturing and materials, we are setting a new standard for sustainability in the retail industry. Additive manufacturing transforms how we produce retail lighting and how we think about its entire lifecycle. From design to disposal, additive manufacturing offers a path to a more sustainable and resource-efficient circular future.
As technology continues to evolve, the possibilities for creating smarter, more efficient, and environmentally friendly lighting solutions expand. At Shoplight, we are committed to leading this change, ensuring that our clients receive the best in modern lighting while contributing to a greener future.
Powered by additive manufacturing, the future of retail lighting is sustainable, efficient, and smart.
10 March 2025

The Impact of Additive Manufacturing on Retail Lighting
31 January 2025

From Battlefields to Peaks:
27 January 2025

From University to Innovation:
24 January 2025

Compact Design, Big Impact.
24 October 2024

Shop Stories - From Vouchers to Variety